Page 565 - Dormer
P. 565
GENERAL HINTS
DRILLING
GENERAL HINTS ON dRILLING
1. Select the most appropriate drill for the application, bearing in mind the material to be machined, the capability of the
machine tool and the coolant to be used.
2. Flexibility within the component and machine tool spindle can cause damage to the drill as well as the component and machine
- ensure maximum stability at all times. This can be improved by selecting the shortest possible drill for the application.
3. Tool holding is an important aspect of the drilling operation and the drill cannot be allowed to slip or move in the tool holder.
4. The correct use of Morse Taper Shank drills relies on an efficient fit between the taper surfaces of the tool and the
tool holder. The use of a soft-faced hammer should be used to drive the drill into the holder.
5. The use of suitable coolants and lubricants are recommended as required by the particular drilling operation. When
using coolants and lubricants, ensure a copious supply, especially at the drill point.
6. Swarf evacuation whilst drilling is essential in ensuring the correct drilling procedure. Never allow the swarf to become
stationary in the flute.
7. When regrinding a drill, always make sure that the correct point geometry is produced and that any wear has been removed.
HOLE SIZE
As geometric, substrate and coating configurations become more advanced, the ability of a drill to produce a more
accurate hole size increases. In general, a standard geometry tool will achieve a hole size to H12. However as the
configuration of the drill becomes more complex the achievable hole size, under favourable conditions, can be as good
as H8. To offer a better insight, listed below are the product types and their achievable hole tolerances:
• HSS General Purpose drills – H12
• HSS / HSS-E Parabolic Flute deep Hole drills – H10
• Solid Carbide High Performance coated – H8/H9
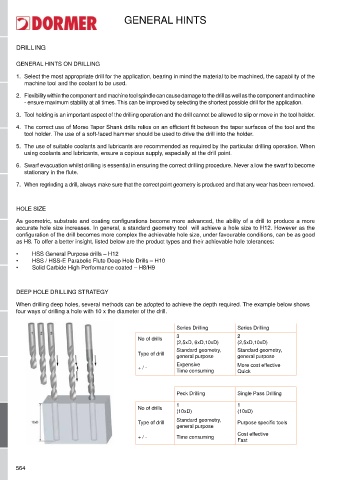
dEEP HOLE dRILLING STRATEGY
When drilling deep holes, several methods can be adopted to achieve the depth required. The example below shows
four ways of drilling a hole with 10 x the diameter of the drill.
Series drilling Series drilling
No of drills 3 2
(2,5xd, 6xd,10xd) (2,5xd,10xd)
Standard geometry, Standard geometry,
Type of drill
general purpose general purpose
Expensive More cost effective
+ / -
Time consuming Quick
Peck drilling Single Pass drilling
1 1
No of drills
(10xd) (10xd)
Type of drill Standard geometry, Purpose specific tools
general purpose
Cost effective
+ / - Time consuming
Fast
564